Python Development Standards: Best Practices for Enterprise-Grade Software
Enterprise-grade Python demands disciplined development standards that guarantee security, compliance, scalability, and long-term maintainability. From PEP 8 and typing to DevOps and CI/CD, these practices reduce risk and accelerate delivery. This guide gives CTOs, engineering managers, and senior developers a practical blueprint to build Python systems that stand up to real-world enterprise demands.
Why Python Needs Development Standards in Enterprise Software
Python now powers healthcare platforms, trading systems, and AI applications—places where mistakes are expensive. Standards are the difference between a clever prototype and a reliable product your company can scale and support for years.
What goes wrong without standards
- Hidden security gaps from inconsistent input validation and dependency hygiene.
- Slow features and outages due to untested, tightly coupled code.
- Hiring drag when new engineers struggle to read and trust the codebase.
- Compliance risk when auditing and traceability are afterthoughts.
Callout: Treat standards like architecture blueprints. You might "ship" without them, but cracks show under production load, audits, and handoffs.
Industry data continues to show Python’s strength across back-end, data, and AI workloads. See the latest adoption patterns in the JetBrains Developer Ecosystem 2024 report.
Need help putting structure in place fast? Explore how we apply standards across AI projects at Zestminds’ AI Development.
Core Python Coding Standards (PEP 8 and Beyond)
What is PEP 8?
PEP 8 stands for Python Enhancement Proposal 8, and it’s the official style guide for Python code. Think of it as the rulebook that ensures every Python developer writes code in a consistent way, no matter which team or company they work in. It doesn’t change how the code runs — instead, it makes sure the code is easy to read, maintain, and scale across large teams.
Key highlights of PEP 8:
- Indentation: 4 spaces per level, never tabs.
- Line length: keep under 79 characters for readability.
- Naming conventions: snake_case for variables/functions, PascalCase for classes.
- Imports: structured and grouped (standard → third-party → local).
- Whitespace rules: use blank lines to separate functions, avoid clutter.
For enterprises, following PEP 8 is the baseline — it prevents "code dialects" inside big teams and keeps onboarding fast. From here, organizations can layer on extra rules like type hints, documentation standards, and CI/CD checks to build enterprise-ready Python codebases.
Reference: The official style guide: PEP 8 — Style Guide for Python Code.
Example: readable, typed, documented
Bad:
def calc(x,y):return x+y
Better:
def calculate_total(price: float, tax: float) -> float:
"""Return the total price including tax."""
return price + tax
Beyond PEP 8: predictability at enterprise scale
- Type hints with mypy to catch integration errors early.
- Docstrings for public modules, classes, and functions to reduce onboarding time.
- Automated formatting with black + linting via flake8 to remove stylistic debates.
- Module boundaries that reflect domain concepts; avoid "god" modules.
Team workflow that enforces standards
- Pre-commit hooks run black, flake8, and mypy locally.
- CI blocks merges when typing, linting, or tests fail.
- Pull requests require code review and a concise design note for complex changes.
Security & Compliance in Enterprise Python Development
Security best practices you should never skip
- Validate all inputs and reject by default; sanitize across boundaries.
- Parameterized queries only; never string-concatenate SQL.
- Never use eval() or exec() on untrusted data.
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit; rotate keys.
- Harden authentication with OAuth2/JWT, proper session lifetimes, and device checks.
- Pin and monitor dependencies; patch known CVEs quickly with automated alerts.
For a practical security checklist, consult OWASP Python Security Guidelines.
Compliance by design
- GDPR/CCPA: data minimization, explicit consent, subject rights workflows, audit trails.
- HIPAA: PHI access controls, logging, breach handling, BAAs with vendors.
- WCAG: accessible interfaces and API responses that support assistive technologies.
See how compliance foundations shape architecture in our HIPAA-compliant AI hospital system case study.
Secure API baseline
- Use FastAPI or Django REST Framework with explicit schemas and validation.
- Adopt zero-trust assumptions between services; sign and verify service-to-service calls.
- Log minimally but meaningfully; avoid secrets and personal data in logs.
Building Scalable & Maintainable Python Applications
Scalability standards
- Async I/O with asyncio or FastAPI for high-concurrency backends.
- Microservices for bounded contexts; deploy independently; observe holistically.
- Caching with Redis for hot paths; add request coalescing to prevent stampedes.
- Horizontal scaling via container orchestration; control state with managed data services.
Maintainability standards
- TDD with pytest and fixtures for reliable, refactor-friendly tests.
- Docs-as-code using Sphinx or mkdocs maintained in the repo.
- Versioning discipline (SemVer), CHANGELOGs, and migration guides for every release.
- Periodic refactoring budget to prevent "interest" on technical debt.
Example of scaling an MVP into a durable platform: the Logoup case study.
Performance optimization techniques
- Profile before optimizing; focus on the slowest 5% of code paths.
- Use vectorized operations (NumPy/Pandas) and bulk queries to trim CPU and I/O.
- Push long-running tasks to queues (Celery/RQ) with idempotent handlers.
- Introduce feature flags to roll out optimizations safely.
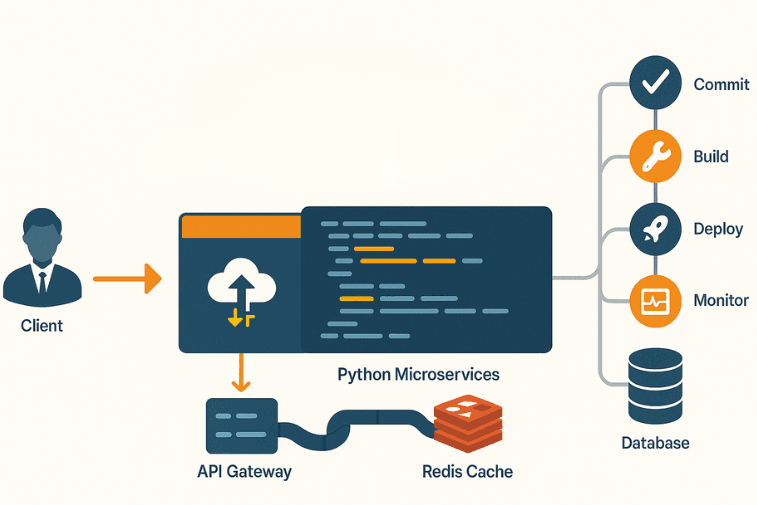
DevOps, Testing & CI/CD Standards for Python Projects
DevOps integration
- Immutable builds with Docker; environment parity from dev to prod.
- Infrastructure as Code (Terraform/Ansible) for repeatable environments.
- Observability with structured logs, tracing, and metrics dashboards.
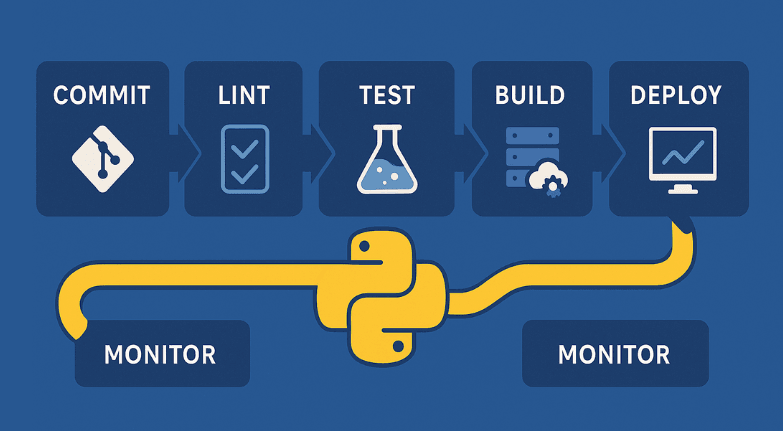
Testing strategy
- Unit tests for logic; integration tests across service boundaries.
- Contract tests for APIs; mocks for third-party systems to stabilize pipelines.
- Non-functional tests: performance, load, and chaos drills.
- Code coverage targets as a guardrail, not a goal; focus on meaningful paths.
CI/CD release safety
- Automated checks: lint, type, test, SBOM generation, security scanning.
- Blue-green or canary deployments with fast rollback.
- Post-deploy health checks and alerting (Prometheus/Grafana).
Why Partner with Zestminds for Enterprise Python Development
- Standards-first delivery: PEP 8, typing, and code-review guardrails from day one.
- Security and compliance engineered into architecture and process.
- Proven scalability with microservices, async backends, and Kubernetes.
- DevOps automation: CI/CD pipelines, IaC, and observability out of the box.
Explore our approach to AI and platform builds at AI Development and see how we scale early-stage products at MVP Development. For content on shipping fast without losing control, read our take on low‑code platforms.
Build Enterprise-Grade Python Software with Zestminds
Ready to turn a working Python product into an enterprise-grade platform? Talk to a Zestminds architect about security, compliance, and scale. Start here: Schedule a consultation or review our enterprise-ready MVP process.
FAQs
What are Python development standards for enterprises?
They are coding, security, and architectural practices, PEP 8, typing, code reviews, CI/CD, and compliance workflows, that keep large codebases reliable and auditable.
Is Python secure enough for enterprise applications?
Yes, when you validate inputs, encrypt data, avoid dangerous constructs like eval(), patch dependencies, and follow guidance such as the OWASP Python Security checklist.
How do standards improve compliance?
Standards build traceability, tested changes, versioned releases, access controls, data minimization, and audit logs, so GDPR/CCPA/HIPAA reviews become process, not panic.
Can Python handle large-scale enterprise systems?
Absolutely. Async frameworks, microservices, caching, queues, and Kubernetes enable global scale with predictable performance.
What tools enforce coding standards?
Automated formatting with black, linting via flake8, static typing with mypy, testing with pytest, and CI pipelines that block merges on failures.
Why choose Zestminds for enterprise Python development?
We deliver standards-first engineering with security, compliance, and scalability built in, plus the DevOps automation to keep it running smoothly.
Additional Resources

Rajat Sharma
About the Author
With over 8 years of experience in software development, I am an Experienced Software Engineer with a demonstrated history of working in the information technology and services industry. Skilled in Python (Programming Language), PHP, jQuery, Ruby on Rails, and CakePHP.. I lead a team of skilled engineers, helping businesses streamline processes, optimize performance, and achieve growth through scalable web and mobile applications, AI integration, and automation.
Stay Ahead with Expert Insights & Trends
Explore industry trends, expert analysis, and actionable strategies to drive success in AI, software development, and digital transformation.